Optical Jukebox Library in the Cloud
We define archival information storage as a mechanism for writing data that can’t be modified or erased, storing information for a very long time (over 50 years), and providing easy retrieval. Information archiving has evolved over the last century; from paper to microfilm, and then to optical discs in jukebox libraries.
Optical discs were introduced in the early 1980s. The Write Once Read Many (WORM) 12-inch discs, introduced by Sony and other companies, provided archiving media that allowed organizations to archive their paper information to optical storage.
CD-ROM discs were introduced by Philips and Sony in 1985. A couple of years later Sony introduced DVD-discs and Magneto-Optical discs. Jukeboxes or Libraries were designed to handle over 500 discs, creating a complete archiving storage system. Blu-ray discs were introduced by Sony in 2003, and became the archiving media standard.
Are you ready for the next step in Archiving?

Cloud-based archival object data storage is the latest technology for information archiving. It uses sophisticated hierarchical storage algorithms and a storage methodology that includes redundancy, backup, and multiple geographic storage points with fail-over. As an example, one cloud storage service expects an annual loss of 0.000000001% of objects. For example, if you store 10,000 objects with a storage facility that utilizes all multiple redundancies, you can on average expect to incur a loss of a single object once every 10,000,000 years.
Cloud-based archiving provides a number of benefits over optical storage libraries. Even though the optical media was archival, it was difficult to guarantee that the drives that read the media and the formats used would be available 50 to 100 years from now. The original 12-inch WORM discs may be holding the data, but the drives for playing these discs are no longer manufactured. With the new storage paradigm, the data can be constantly moved to the next generation of storage thus assuring availability in the future.
Performance is actually improved with cloud based storage. Optical drives provide data transfer rates of about 36 Mbps, and have very high latency when the disc has to be moved to the reader (over 3 secs). The cloud data systems have data rates that are limited by the Internet speeds and latency in milliseconds. For example, Verizon provides internet speeds of up to 500/500 Mbps.
Large organizations can certainly create their own local archival systems, but the remote storage servers and storage points available from very large big data facilities can provide better security and redundancy. Storage in the Cloud, has now made this technology available to anyone.
There are cloud storage systems such as those available from Dropbox, Google Drive, Amazon, Microsoft OneDrive, and other remote data storage systems, but there is a difference between standard cloud “storage” and “Cloud Archiving”. Cloud archiving includes intelligent data handling. It is an automated processes that helps you “integrate” this storage technology in an intelligent and intuitive manner. More than just “connecting” to the cloud, it is important to determine how to manage the process of identifying and processing data for migrating and archiving to the these remote storage servers.
Policy Based Archiving
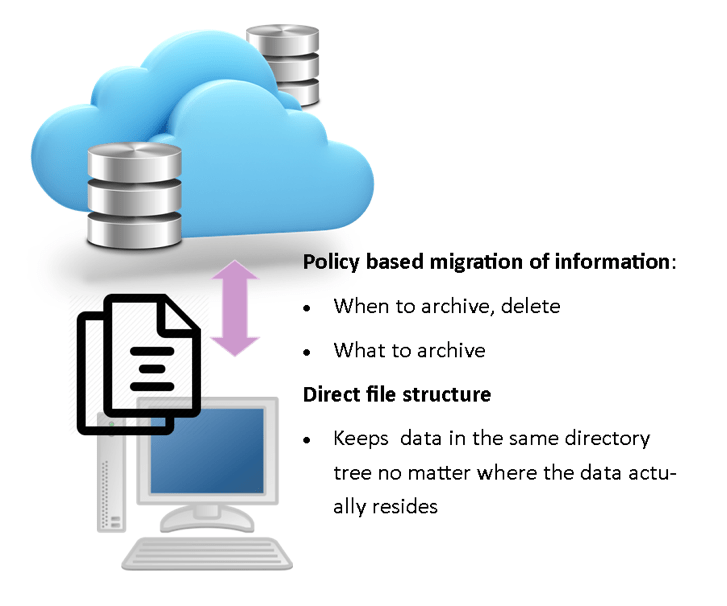
Automated policy based archiving software, that has been used for optical jukebox libraries, is now used for cloud-based archiving. It provides the database indexing required for unstructured data (objects), as well as providing the decision about when and where to move the data. Each file or folder can be assigned a set of policies. The policies include: what to archive, when to archive, and where to archive.
The latest hierarchical storage managers provide almost transparent data migration. This is all very similar to archiving data to a blue-ray optical jukebox library in that all the files are udf image files, creating a virtual jukebox library in the cloud.
There is even an option of maintaining the file structure that you have on your hard drive or network server after the files are actually moved to the cloud archiving server. The file structure is still in the same directory. This is different than moving your information to dropbox or Google drive. The files still look like they are in the same place. The pointers to the file have just moved to the cloud storage. It provides a single path to all your files.
Cloud Archiving Benefits
“Cloud Archiving” is the new paradigm for data storage. It provides an alternative to traditional file- and block based storage. Advantages of Cloud object storage compared to traditional storage are its scalability, its method for processing metadata and the ability to simplify data protection. For these reasons Cloud archiving is perfectly suited for inactive data and data which needs to be archived. Data Objects can be located on an external storage device which can be accessed by internet/intranet connection using internet protocols. This makes it useful for achieving off site replication for disaster recovery as well as providing secure remote access to data from any computer.
Need help selecting the archiving system that’s best for you? Please contact us at 800-431-1658 in the USA, or at 914-944-3425 everywhere else, or use our contact form.