Mobile phones are the new Credential
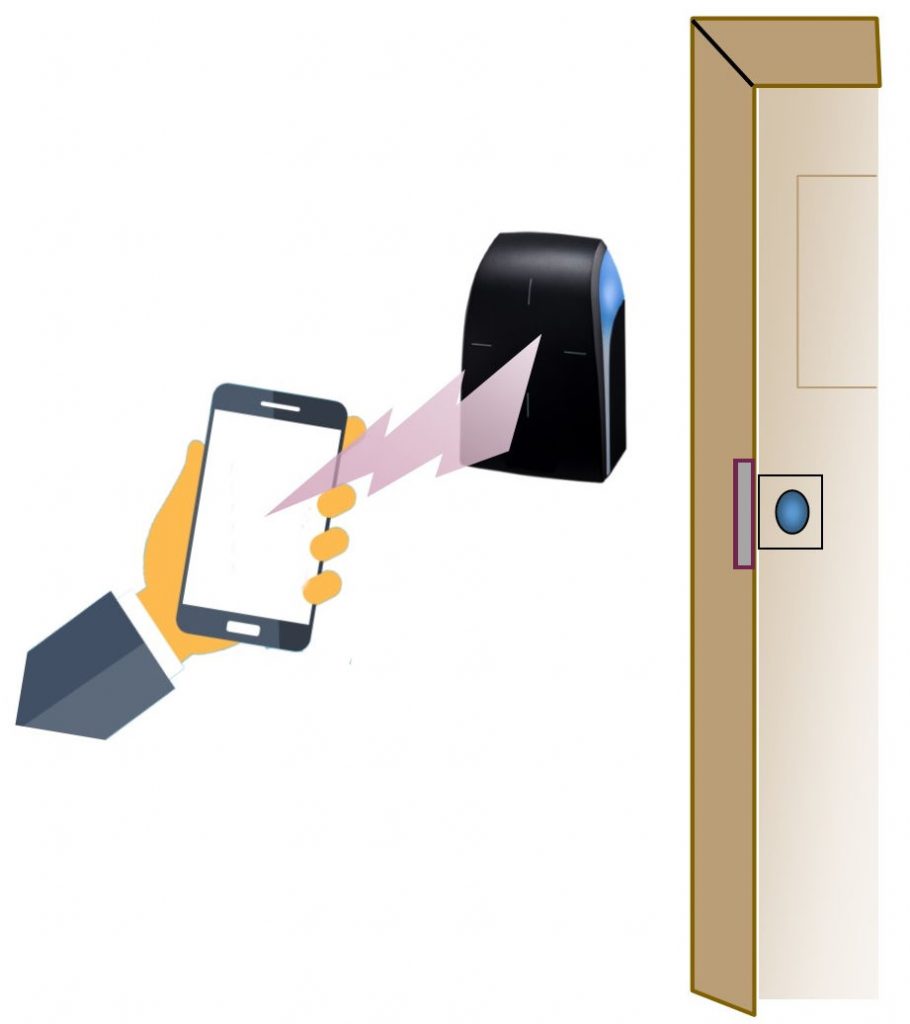
Have we reached the tipping point? Will our smartphones become our new door key? It all depends on the number of smartphones in the population. One survey indicates that 81% of the US population owns a smartphone. As the percentage increases, there will be enough smartphones to enable the use of mobile keys. It is quite likely that this will happen in the near future.
If everyone in your organization, apartment complex or school has a smartphone, you have reached the tipping point. You can use your smartphone as a mobile credential to open your doors.
Many smartphones use biometrics to unlock the phone. This security feature can make them more secure than carrying a card credential. This article describes how mobile credentials work in access control systems.
What is a Mobile Credential
A mobile credential is an authorization token much like a Prox card or keyfob. The ID number is held in your smartphone instead of a card. That’s why we call it a mobile credential. Just like other types of credentials, it contains a unique number that can be used as the electronic key to open a door with an electric lock. The smartphone can connect to a door reader using Bluetooth, NFC, or even WiFi. Bluetooth (BLE) is the most common type of communication used in the security market.
Mobile credentials are more likely to be brought with you than a card that could be forgotten at home. The smartphone is a personal device that has become a part of our regular daily activity. Because of its importance, it is unlikely to be given to another person. The added security of unlocking the smartphone adds additional security against misuse.
Mobile Credentials Use Bluetooth

Bluetooth wireless technology is used to connect the smartphone to the door reader. Bluetooth was invented in Sweden in 1989. It was initially developed to provide a wireless connection to headsets. Bluetooth connections operate at frequencies around 2.4GHz. It uses frequency-hopping spread spectrum that improves the reliability of information transmission. Spread-spectrum also has the characteristic of being more secure than fixed frequency transmission because the signal is tough to intercept.
Bluetooth range is determined by the power available to the transmitter, the antenna, and the propagation conditions. For example, the signal can be attenuated if it passes through a wall. Classes of power and range have been established. Power and distance vary from Class 1 that uses about 100mW and has an operational distance of about 100m (328 ft.) to Class 4 with a range of approximately 0.5m (1.6 ft.)
The Bluetooth specifications have been defined by the Bluetooth Special Interest Group (SIG). The specifications include among other things the protocols and how power is used. Bluetooth 1 was developed in 1998. Over the years new specifications were introduced that improved the interconnectivity of devices, increased data speed, and made better use of available power and improved the range. Bluetooth 5 is a new version announced in 2016. The specification is used by many of the latest Android and iPhones. The new specification includes Bluetooth Low Energy (BLE) which reduces the power required while increasing data rates and increasing range to over 400 m (1,300 ft.).
How Door Readers Work with Mobile Credentials
Bluetooth is used to connect the smartphone to the door reader. The Isonas IP readers and the Hartmann door access control system includes a Mobile Credential option. The door readers have a maximum range of about 65 ft.
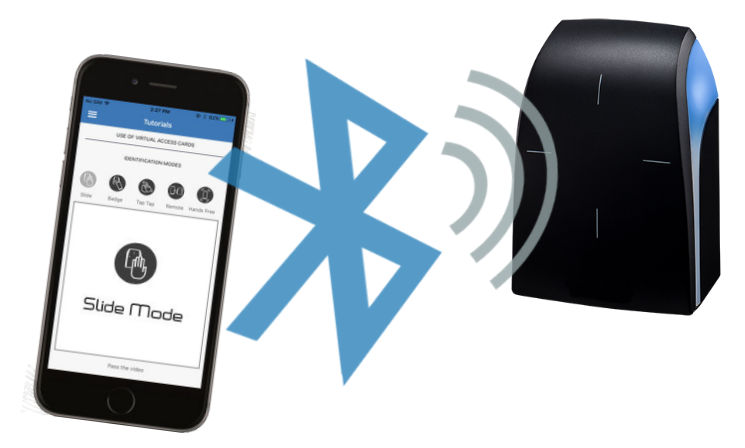

The smartphone and the Bluetooth enabled door reader use many of the features defined by the Bluetooth protocol. The door reader is continuously looking for the smartphone that’s running the mobile app. When the two devices are in range, they transfer the device name, device class, list of available services, and additional significant information required to identify the user uniquely. This transfer retrieves the unique number provided by the smartphone (key).
The smartphone and the Bluetooth enabled door reader use many of the features defined by the Bluetooth protocol. The door reader is continuously looking for the smartphone that’s running the mobile app. When the two devices are in range, they transfer the device name, device class, list of available services, and additional significant information required to identify the user uniquely. This transfer retrieves the unique number provided by the smartphone (key).
Each smartphone includes a unique 48-bit address which can be used as the key. This identification number is like the ID number that is provided by the card credential. The smartphone app controls the transfer of the identification number to the door reader. The ID number is transferred from the door reader to the controller where it is compared to the list of users. If the ID number is accepted, it will unlock the door. The list of users is maintained using the door access management software.
There are various ways to initiate communication between the smartphone and the door reader. In most cases, the phone is simply placed close to the reader just like using a card credential. The Isonas IP reader requires the app to be activated when you are near the door. The Hartmann control system includes a number of other ways to activate the connection. For example, one option is to keep the phone in your pocket and wave your hand over the reader. This motion causes the reader to query your smartphone. Another mode connects the smartphone to the reader as you approach the door. Your environment and security requirements will determine the best way to open the door using your smartphone.
Security of Mobile Credentials

The latest Bluetooth enabled door readers, such as the ones used by Hartmann Controls door access control system, include many advanced security features and modes of identification. Besides using the security provided by Bluetooth spread-spectrum communication, the system uses encryption and obfuscation methods to protect the app in the smartphone, and the data stored in the door reader. The encryption process protects data from hacking. It makes it difficult to read the data without knowing the key. Obfuscation adds another level of security. This involves using a puzzle or other challenge that locks the key itself from the hacker. Additional protection is provided by using multi-factor authentication and maintaining security audits.
The latest Bluetooth enabled door readers, such as the ones used by Hartmann Controls door access control system, include many advanced security features and modes of identification. Besides using the security provided by Bluetooth spread-spectrum communication, the system uses encryption and obfuscation methods to protect the app in the smartphone, and the data stored in the door reader. The encryption process protects data from hacking. It makes it difficult to read the data without knowing the key. Obfuscation adds another level of security. This involves using a puzzle or other challenge that locks the key itself from the hacker. Additional protection is provided by using multi-factor authentication and maintaining security audits.
Using a smartphone with biometric authentication can improve door access security. We have known for a long time that Biometrics provides a more secure way to open the door than using a card credential that someone carries. The card can be lost or given to someone else. It is less likely for the mobile smartphone credential to be misused in this way. Since some smartphones have embedded biometrics, it can be used to increase the security of door access systems.
Summary of Mobile Credentials
Mobile credentials are used in access control systems instead of prox cards or keyfobs. They are the latest way to open the door. Instead of using card credentials, they use your mobile smartphone as the key. The smartphone uses Bluetooth communication to the door readers. It is secure and easy to use. It is more convenient than card credentials and biometric readers. Smartphones are used by most people, so they are becoming more popular in access control applications.
For help selecting the right door access control system, please contact us at 800-431-1658 in the USA, or at 914-944-3425 everywhere else, or use our contact form.